Loading Port:Shanghai
Payment Terms:TT or LC
Min Order Qty:1 unit
Supply Capability:1 unit/month
Forklift Description:
A forklift truck (also called a lift truck, a fork truck, or a forklift) is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th century by various companies including the transmission manufacturing company Clark and the hoist company Yale & Towne Manufacturing. Following World War II the use and development of the forklift truck has greatly expanded worldwide. Forklifts have become an indispensable piece of equipment in manufacturing and warehousing operations.
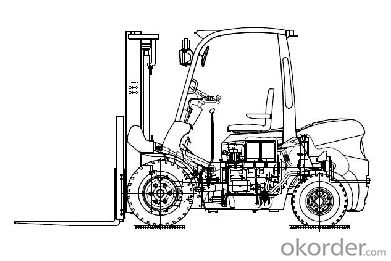
Image of an electric forklift with component descriptions
Truck frame - is the base of the machine to which the mast, axles, wheels, counterweight, overhead guard and power source are attached. The frame may have fuel and hydraulic fluid tanks constructed as part of the frame assembly.
Counterweight - is a mass attached to the rear of the forklift truck frame. The purpose of the counterweight is to counterbalance the load being lifted. In an electric forklift the large lead-acid battery itself may serve as part of the counterweight.
Cab - is the area that contains a seat for the operator along with the control pedals, steering wheel, levers, switches and a dashboard containing operator readouts. The cab area may be open air or enclosed but it is covered by the cage-like overhead guard assembly. When enclosed, the cab may also be equipped with a cab heater for cold climate countries along with a fan or air conditioning for hot weather.
Overhead guard - is a metal roof supported by posts at each corner of the cab that helps protect the operator from any falling objects. On some forklifts, the overhead guard is an integrated part of the frame assembly.
Power source - may consist of an internal combustion engine that can be powered by LP gas, CNG, gasoline or diesel fuel. Electric forklifts are powered by either a battery or fuel cells that provides power to the electric motors. The electric motors used on a forklift may be either DC or AC types.
Tilt cylinders - are hydraulic cylinders that are mounted to the truck frame and the mast. The tilt cylinders pivot the mast backward or forward to assist in engaging a load.
Mast - is the vertical assembly that does the work of raising and lowering the load. It is made up of interlocking rails that also provide lateral stability. The interlocking rails may either have rollers or bushings as guides. The mast is driven hydraulically, and operated by one or more hydraulic cylinders directly or using chains from the cylinder/s. It may be mounted to the front axle or the frame of the forklift. A 'container mast' variation allows the forks to raise a few meters without increasing the total height of the forklift. This is useful when double-loading pallets into a container or under a mezzanine floor.
Forklifts are rated for loads at a specified maximum weight and a specified forward center of gravity. This information is located on a nameplate provided by the manufacturer, and loads must not exceed these specifications. In many jurisdictions it is illegal to remove or tamper with the nameplate without the permission of the forklift manufacturer.
An important aspect of forklift operation is that most have rear-wheel steering. While this increases maneuverability in tight cornering situations, it differs from a driver’s traditional experience with other wheeled vehicles. While steering, as there is no caster action, it is unnecessary to apply steering force to maintain a constant rate of turn.
Another critical characteristic of the forklift is its instability. The forklift and load must be considered a unit with a continually varying center of gravity with every movement of the load. A forklift must never negotiate a turn at speed with a raised load, where centrifugal and gravitational forces may combine to cause a disastrous tip-over accident. The forklift are designed with a load limit for the forks which is decreased with fork elevation and undercutting of the load (i.e., when a load does not butt against the fork "L"). A loading plate for loading reference is usually located on the forklift. A forklift should not be used as a personnel lift without the fitting of specific safety equipment, such as a "cherry picker" or "cage".
Forklifts are a critical element of warehouses and distribution centers. It’s imperative that these structures be designed to accommodate their efficient and safe movement. In the case of Drive-In/Drive-Thru Racking, a forklift needs to travel inside a storage bay that is multiple pallet positions deep to place or retrieve a pallet. Often, forklift drivers are guided into the bay through guide rails on the floor and the pallet is placed on cantilevered arms or rails. These maneuvers require well-trained operators. Since every pallet requires the truck to enter the storage structure, damage is more common than with other types of storage. In designing a drive-in system, dimensions of the fork truck, including overall width and mast width, must be carefully considered.
Forklift Specification:
Load center mm | 500mm | |
Power type | Battery | |
Max.lifting speeds | 285mm/s | |
(with load)mm/s | ||
Max.Driving speeds | 13.5/15km/h | |
(with without load)km/h | ||
Max.Towing speeds | 12kN | |
(with load)kN | ||
Gradeability(with load)% | 15% | |
Lifting height mm | 3000mm | |
Free lift mm | 75mm | |
Tilting angles |
| |
Min. turning radius mm | 2400mm | |
Min. right angle aisle width mm | 3900mm | |
Min. under-clearance mm | 140mm | |
Dimensions | A Overall length (inincluding fork) mm | 3745 |
B Overall width mm | 1240 | |
H Overall height(mast lowered) mm | 2200 | |
H2 Overall height(mast extend) mm | 4260 | |
H3 Overall height to overhead guard mm | 2200mm | |
B3 Fork width mm | 125mm | |
H4 Fork thickness mm | 50mm | |
A3 Fork length mm |
| |
A1 Fork overhang mm | 495mm | |
A2 Wheel base mm | 1700mm | |
Tread | Front tread mm | 1000mm |
Rear tread mm | 980mm | |
Tyre | Front tyre | 28×9-15mm |
Rear tyre | 18×7-8mm | |
Total weight kg | 5160 | |
Motor | Traction motor | XQ-10-1C |
Lifting motor | XQD-13-3S | |
Battery | Battery type | 40-DA-500 |
Battery voltage/Capacity V/Ah | 80/500 | |
Forklift Images:


FAQ of forklift:
Q: What’s the function of forklift?
A: A forklift truck (also called a lift truck, a fork truck, or a forklift) is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th century by various companies including the transmission manufacturing company Clark and the hoist company Yale & Towne Manufacturing. Following World War II the use and development of the forklift truck has greatly expanded worldwide. Forklifts have become an indispensable piece of equipment in manufacturing and warehousing operations.
Q: What’s the general operations of forklift:
A: Forklift cab with control layout.
Forklifts are rated for loads at a specified maximum weight and a specified forward center of gravity. This information is located on a nameplate provided by the manufacturer, and loads must not exceed these specifications. In many jurisdictions it is illegal to remove or tamper with the nameplate without the permission of the forklift manufacturer.
Q: What are the Forklift safety Standards?
A: 1, Forklift safety is subject to a variety of standards world wide. The most important standard is the ANSI B56—of which stewardship has now been passed from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) to the Industrial Truck Standards Development Foundation after multi-year negotiations. ITSDF is a non-profit organization whose only purpose is the promulgation and modernization of the B56 standard.
2, Other forklift safety standards have been implemented in the United States by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and in the United Kingdom by the Health and Safety Executive.
3, Driver safety: In many countries forklift truck operators must be trained and certified to operate forklift trucks. Certification may be required for each individual class of lift that an operator would use.